Article Index
| News |
| Page 2 |
| Page 3 |
| Page 4 |
| Page 5 |
| Page 6 |
| Page 7 |
| Page 8 |
Times health - Saturday
PIONEER THEN, LEADER NOW
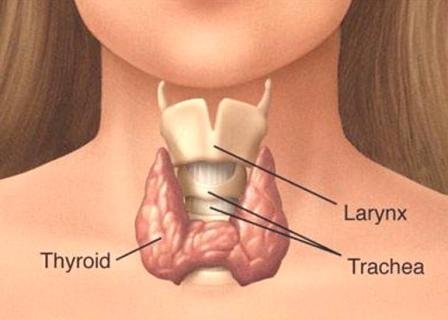
UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF THE THYROID GLAND
"It was only in 1656 that the thyroid gland was at last located and identified by Thomas Wharton, an anatomist. It is a butterfly shaped small gland present in the front of the neck. This gland produces mainly two types of hormones - Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine. These hormones help in the functioning of many systems of the body. Thyroid is divided into two parts, connected by isthmus, whichacts as a bridge between the two halves. The Thyroid gland in a woman's body is larger than those in a man's body. Its functioning is controlled by the pituitary gland that secretes thyroid stimulating hormone. Diseases related to the thyroid gland, caused due to production of less hormone or more hormones are common across the world," says Dr V Mahendran, MBBS, DCH., D.Ac, Ph.D.(A.M),at the Thyroid Centre.
How does the thyroid gland work ?
The thyroid gland works like a tinny factory that uses iodine (mostly from food items such as seafood and salt) to produce thyroid hormone. These hormones help to regulate the body's metabolism and affect the growth and other important functions of the body
99.9 percent of thyroid hormones are stored in Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) and 0.1 percent of thyroid hormones are stored in Saliva, gastro intestine tract, muscles and heartrespectively. The hormone with the biological power is actually T3. Once released from the thyroid gland into the blood, a large amount of T4 is converted to T3 - the active hormone that affects the metabolism of cells throughout our body.
TYPES OF THYROID DISEASE
Hypothyroidism: If the thyroid itself is underactive, or if the regulators of the thyroid gland are not functioning properly, this can result in hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism: If the thyroid is overactive, or if the regulators of the thyroid gland are pushing the thyroid to thyroid to produce too much hormone, this can lead to hyperthyroidism.
TREATMENT FOR THYROID DISEASES
"Due to consumption of food items without iodine, like water, milk fruits, vegetables or green leaves, both human beings and animals develop thyroid -related diseases. These are highly prevalent in Himalayas, Vindhyas, Nilgiris, Kerala, Karnataka and several other hilly regions in India. This can be eradicated if people consume iodine-enriched salt," elabrates Dr V Mahendran.
Depending on the severity and other specifications of the disease, it can treated using modalities like oral medication, surgery or radioactive therapy.
MEDICATIONS
Dr. V. Mahendran says, "Medication may be used to treat hyperthyroidism to reduce the production of thyroid hormone, its release from the gland and/or to treat the signs and symptoms that occur in hyperthyroidism such as rapid heartbeat. In hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone is used to replace the inadequacy of thyroid hormone. Occasionally, in the case of a large goitre, thyroid hormone replacement may be given in small does in attempt to shrink the gland size. It should be mentioned that there are natural thyroid compounds available in the market. These vary in their effects and dosage and are beyond the scope of this discussion. Steroids and other anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, may also be used to reduce inflammation of the thyroid gland."
SURGERY
Surgery is the treatment of choice when the thyroid gland is compressing the airway, resulting in difficulty in breathing or swallowing. In addition, surgery can be performed to remove a nodule that is overactive, a goitre that is disfigured, or when cancer is possibility. Depending on the reason for the surgery, part of a lobe, a whole lobe or the whole thyroid (perhaps with surrounding tissue) gland may be removed. When the entire thyroid gland is removed, medical replacement with synthetic thyroid replacement is required.
RADIOACTIVE ABLATION
When hyperthyroidism is not responding to medication, radioactive ablation may be tried. The iodine in this situation is labelled with a tracer that destroys the thyroid tissue. Ablation is used in cases of hyperthyroidism that do not respond to medication, particularly Grave's disease. This form of therapy is also used along with surgery to treat certain forms of thyroid cancer.
OTHER DISEASES RELATED TO THYROID
- Vitiligo (White patches)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (joint pain and swelling)
- Addison's disease, diabetes
- Pernicious Anaemia
- Low BP and High BP
THYROID TESTS
Blood Test (T3, T4, TSH, FT3, FT4, ATG, AMA)
Scans: Ultrasound, CT, MRI, PET Scan
FNAC - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology


Honorary Consultant To
- Acupunture Foundation, Coimbatore - 641012
- Om Yoga Center, Coimbatore - 641002
- Nature Cure Center, Coimbatore - 641012
- Indian REIKI Foundation, Coimbatore - 641012
- Electro Homoepathy Council, Coimbatore - 641045
Works In Association With
- Indian Thyroid Society : Life Member
- Covai Scan Center, Tatabad, Coimbatore.
- Sai Pathological Lab, Tatabad, Coimbatore.
- Nuclear Department, Coimbatore Hospital, Coimbatore.
- Ellen Hospital, Coimbatore.
- Thyro Care - A Thyroid Hormone Testing Lab(for Blood test)
Experiences
- 'Life Member', IMA (Indian Medical Association), Coimbatore, Tamilnadu
- 'Treasurer', IMA(Indian Medical Association), Nilgiris Branch, Tamilnadu [from 1985-1989]
- 'Secretary', IMA(Indian Medical Association), Nilgiris Branch, Tamilnadu [from 1989-1990]
- 'Member', IMA State Council [from 1990-1991]
Contact Us
Address: No 5, Level I Nataraj Medicare,
No 1, Cowley Brown Road,
Opp. to Central Theatre,
R.S Puram
Coimbatore - 641 002.
Tel: 0422 - 4214320.
Cell: 99424 - 80100.
Email: mahenthyroid@gmail.com